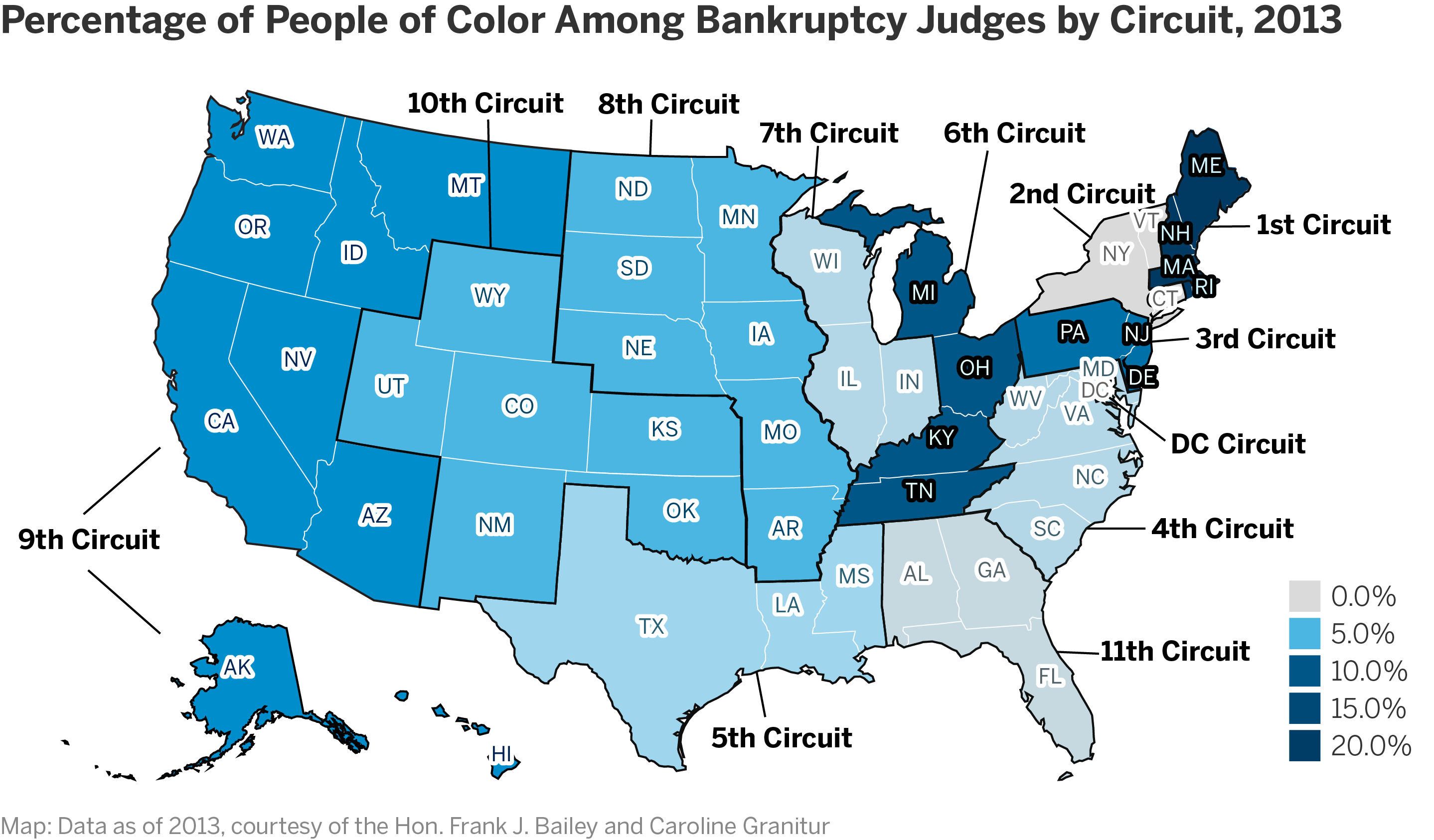
Bankruptcy courts are units of the federal district courts. They handle bankruptcy filings by individuals, entities, and corporations to discard debt or make a plan to pay back their debts. The Administrative Office of the U.S. Courts reports that as of 2018, there are 350 authorized bankruptcy judgeships and 90 bankruptcy courts in the federal judiciary.
According to the Administrative Office of the U.S. Courts, in fiscal year 2018 there were 773,375 bankruptcy petitions filed, 816,006 bankruptcy petitions terminated, and 1,027,477 bankruptcy petitions pending. This was the lowest total of bankruptcy petitions filed since 2007.
There are several different types of bankruptcy. Chapter 7 allows for individuals or businesses to liquidate their assets. Chapter 9 gives the opportunity for municipalities to reorganize. Chapter 11 allows for businesses or organizations to reorganize. Chapter 12 grants debt relief to family farmers and fishermen. Chapter 13 is for individuals to adjust their debts and pay them back over time. Lastly, Chapter 15 provides for bankruptcy in cases where there are multiple parties involved who are based in more than one country.
For information on salaries for bankruptcy judges, see the Federal Judicial Center.